Introduction: Why DMAIC is Essential for Process Improvement
In today’s competitive business environment, organizations strive to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction. DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) is a structured problem-solving approach within Lean Six Sigma that enables teams to drive process improvements systematically.
At Lean Six Sigma Hub, we empower professionals through self-paced Lean Six Sigma training, providing them with the tools and frameworks needed to achieve measurable results. One of the most effective ways to execute a DMAIC project successfully is by using a DMAIC Project Planner—a structured framework that ensures each phase is completed efficiently and effectively.
In this article, we’ll explore how a DMAIC Project Planner enhances project execution, step-by-step best practices, and why integrating project management within the Improve phase leads to sustainable success.
What is the DMAIC Project Planner?
The DMAIC Project Planner is a structured tool that guides Lean Six Sigma practitioners through each phase of their project. It serves as a blueprint for process improvement, helping teams stay organized, focused, and data-driven.
By following this planner, teams can:
✔ Identify and define key business problems.
✔ Collect and analyze relevant data.
✔ Implement data-backed solutions.
✔ Monitor and control improvements for long-term sustainability.
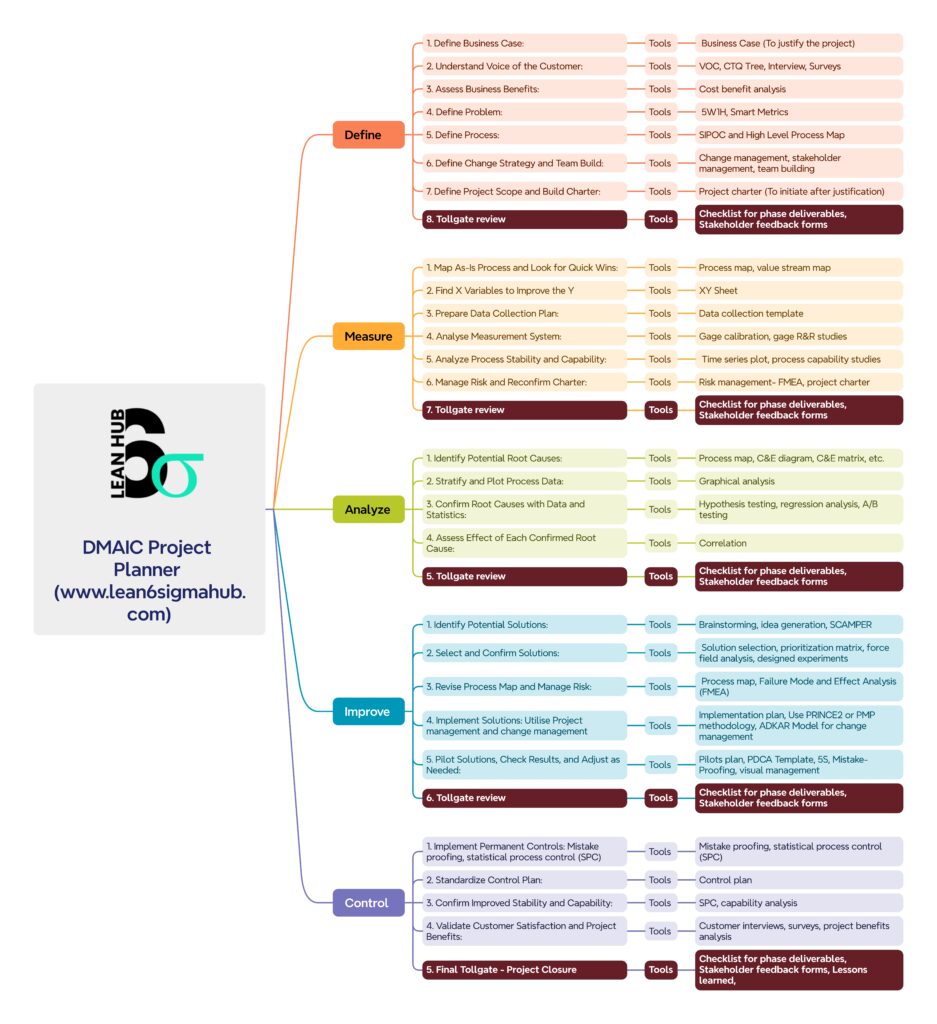
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the DMAIC Project Planner
1. Recognize: Identifying Improvement Opportunities
Before initiating a Lean Six Sigma project, the first step is to recognize areas of improvement. The planner provides tools to:
✅ Gather stakeholder feedback via focus groups and surveys.
✅ Analyze Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and historical data.
✅ Conduct process observations to detect inefficiencies.
✅ Benchmark performance against industry best practices.
✅ Identify customer complaints and pain points.
🔹 Key Tools: KPI analysis, observation checklists, benchmarking reports, customer survey results.
2. Define: Establishing Project Scope and Objectives
The Define phase ensures that all stakeholders are aligned on project goals. The planner helps teams:
✅ Develop a Business Case to justify the project.
✅ Capture the Voice of the Customer (VOC) to identify key needs.
✅ Map out current processes using SIPOC diagrams.
✅ Define the problem statement and objectives.
✅ Establish a Project Charter to document scope, timeline, and team roles.
🔹 Key Tools: SIPOC, CTQ trees, project charters, business case templates.
3. Measure: Collecting and Analyzing Data
The Measure phase focuses on understanding the current state of the process. The planner includes:
✅ Mapping the As-Is Process with value stream mapping.
✅ Identifying key variables that impact performance.
✅ Developing a data collection plan with sampling strategies.
✅ Conducting Measurement System Analysis (MSA) to ensure data accuracy.
✅ Assessing process stability and capability using statistical tools.
🔹 Key Tools: Value stream maps, XY sheets, gage R&R, control charts, process capability analysis.
4. Analyze: Identifying Root Causes
This phase focuses on finding the true causes of process inefficiencies. The planner provides:
✅ Cause-and-Effect (Fishbone) Diagrams to map out potential factors.
✅ 5 Whys Analysis to drill down to root causes.
✅ Pareto Analysis to prioritize critical issues.
✅ Statistical Hypothesis Testing to validate findings.
✅ Correlation and Regression Analysis to quantify relationships between variables.
🔹 Key Tools: C&E diagrams, Pareto charts, statistical hypothesis tests, regression analysis.
5. Improve: Implementing and Managing Change
The Improve phase is where solutions are developed and tested. Traditionally, DMAIC focuses on technical improvements, but the DMAIC Project Planner enhances this phase by integrating Project Management.
✅ Identifying and Selecting Solutions
– Brainstorming, prioritization matrices, SCAMPER techniques.
✅ Integrating Project Management for Structured Implementation
– Developing a Project Plan (Gantt Chart, WBS, CPM).
✅ Allocating resources and budgeting (Cost-Benefit Analysis).
✅ Implementing a Stakeholder Communication Plan (RACI matrix).
✅ Managing risk and change adoption (FMEA, ADKAR, Kotter’s Change Model).
✅ Testing and Refining Solutions
– Piloting solutions using PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act).
🔹 Key Tools: Gantt charts, cost-benefit analysis, stakeholder analysis, ADKAR, risk registers, FMEA.
6. Control: Ensuring Long-Term Sustainability
To sustain improvements, organizations must establish control mechanisms. The planner emphasizes:
✅ Implementing Permanent Controls
– Standard operating procedures (SOPs), mistake-proofing (Poka-Yoke).
✅ Developing a Standardized Control Plan
– Control charts, dashboards for KPI monitoring.
✅ Confirming Stability and Capability
– Ongoing process capability assessments.
✅ Validating Customer and Business Impact
– Measuring ROI, tracking customer satisfaction post-implementation.
🔹 Key Tools: Control plans, SPC charts, capability analysis, customer feedback surveys.
7. Sustain: Embedding Continuous Improvement Culture
Beyond DMAIC, the planner encourages organizations to establish a culture of continuous improvement by:
✅ Fostering Employee Engagement
– Training and development programs, mentorship initiatives.
✅ Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
– Defining accountability and ownership.
✅ Conducting Regular Review Meetings
– Auditing processes to prevent performance decline.
🔹 Key Tools: Continuous improvement playbooks, KPI dashboards, mentorship programs.
Why Use the DMAIC Project Planner?
✔ Ensures Structure & Clarity – Keeps projects on track with a step-by-step roadmap.
✔ Integrates Data-Driven Decision-Making – Promotes objective analysis at every stage.
✔ Enhances Collaboration – Encourages alignment between stakeholders.
✔ Facilitates Change Management – Addresses risks and adoption challenges.
✔ Leads to Sustainable Improvements – Prevents regression and fosters long-term success.
Get Started with Lean Six Sigma Training
At Lean Six Sigma Hub, we provide self-paced Lean Six Sigma training to help professionals master the DMAIC methodology. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced practitioner, our courses are designed to equip you with real-world applications and case studies.
🚀 Ready to take your Lean Six Sigma skills to the next level?
Explore our training programs and start leading successful process improvement projects today!








