Introduction
Lean Six Sigma certification is a globally recognized credential that equips professionals with the tools and methodologies needed to enhance process efficiency, minimize defects, and drive continuous improvement. Whether you’re a project manager, business analyst, or quality assurance specialist, obtaining a Lean Six Sigma certification can boost your career prospects and improve organizational performance.
In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about Lean Six Sigma certification, including its benefits, certification levels, key methodologies, and practical implementation. Inline charts and graphs will be provided to visualize critical concepts, making this guide easy to follow and actionable.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that combines Lean principles (waste reduction) with Six Sigma methodologies (variation reduction) to enhance operational efficiency and quality. It follows a structured framework, primarily using the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology to solve process-related problems.
Levels of Lean Six Sigma Certification
Lean Six Sigma certification is divided into different levels, known as “belts,” each representing a higher level of expertise. Below is a visual representation of the certification hierarchy:
Lean Six Sigma Certification Belt Levels
I’ll generate a bar chart that visually represents the hierarchy and scope of each Lean Six Sigma belt level.
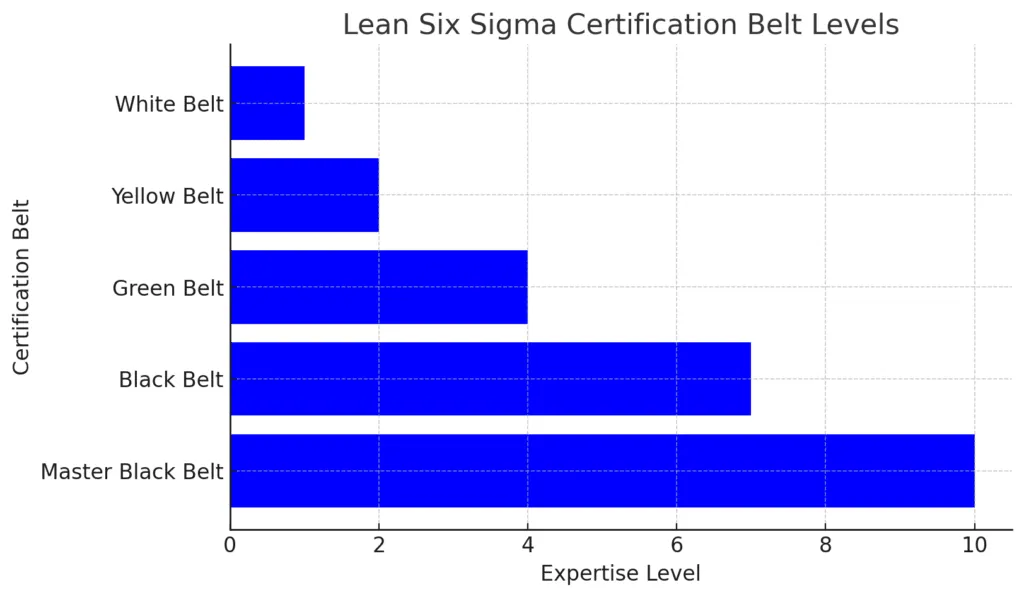
The chart above illustrates the different Lean Six Sigma certification levels, where expertise and responsibilities increase as you progress from White Belt to Master Black Belt.
Overview of Each Certification Level
- White Belt – Basic understanding of Lean Six Sigma concepts. Ideal for beginners.
- Yellow Belt – Supports projects by collecting data and identifying process inefficiencies.
- Green Belt – Leads small projects, focusing on process improvements using DMAIC.
- Black Belt – Expert-level professional leading complex improvement projects.
- Master Black Belt – Coaches and mentors Black Belts and Green Belts, guiding Lean Six Sigma initiatives at the enterprise level.
Key Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Certification
Lean Six Sigma certification offers numerous benefits for individuals and organizations. Below is a pie chart representing key advantages
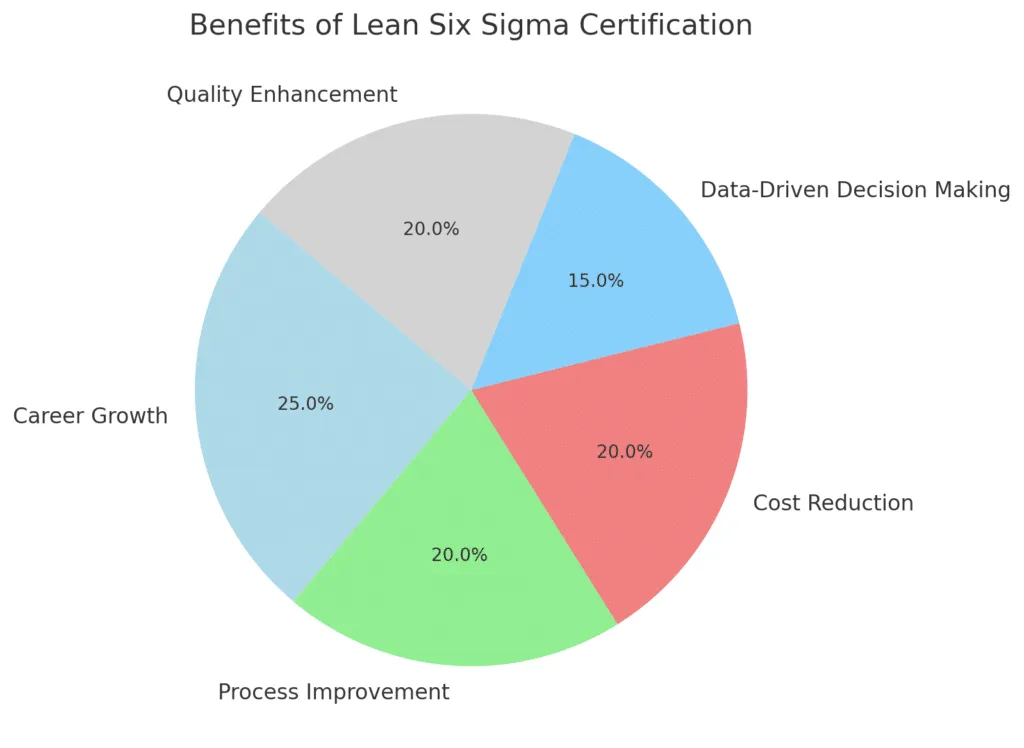
The pie chart above highlights the key benefits of Lean Six Sigma certification:
- Career Growth (25%) – Enhances job prospects and salary potential.
- Process Improvement (20%) – Helps optimize business operations and efficiency.
- Cost Reduction (20%) – Reduces defects and waste, improving financial performance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making (15%) – Encourages fact-based problem-solving.
- Quality Enhancement (20%) – Leads to higher customer satisfaction through process control.
Lean Six Sigma Methodology: The DMAIC Framework
The DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework is the core methodology used in Lean Six Sigma projects. Below is a breakdown of each phase along with a visual representation.
DMAIC Process Breakdown
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Define | Identify the problem, set goals, and outline project scope. |
| Measure | Collect data to understand current performance. |
| Analyze | Determine root causes of defects using statistical analysis. |
| Improve | Implement solutions to optimize processes. |
| Control | Monitor results and sustain improvements. |
Now, let’s visualize the DMAIC process flow
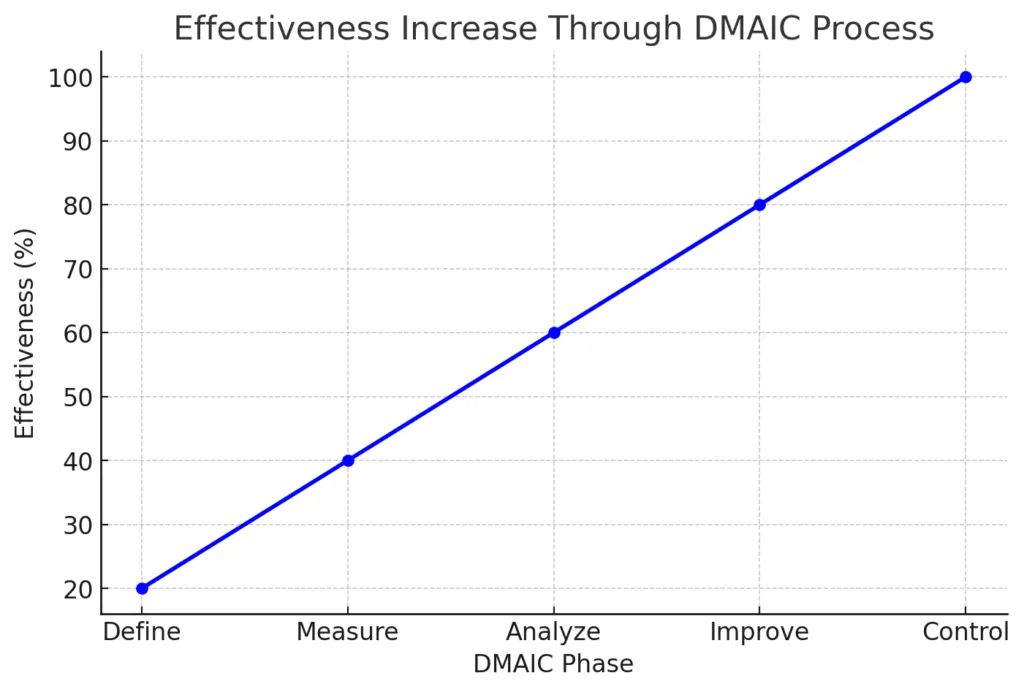
The graph above illustrates how effectiveness improves progressively through each phase of the DMAIC process, reaching 100% at the Control stage when improvements are sustained.
How to Get Lean Six Sigma Certified
Step-by-Step Guide to Certification
- Choose the Right Certification Level – Determine which belt aligns with your career goals.
- Select an Accredited Training Provider – Ensure the certification is from a recognized institution.
- Complete the Training – Engage in coursework, case studies, and real-world applications.
- Pass the Certification Exam – Demonstrate knowledge through rigorous testing.
- Apply Lean Six Sigma in Projects – Gain hands-on experience by leading or participating in process improvement projects.
Conclusion
Lean Six Sigma certification is a powerful credential that enhances career opportunities, improves business efficiency, and fosters data-driven decision-making. By mastering the DMAIC methodology and applying Lean Six Sigma principles, professionals can significantly impact organizational success.
Are you ready to take the next step in your Lean Six Sigma journey? Start exploring certification programs today and unlock new career opportunities! 🚀
Key Takeaways:
✅ Lean Six Sigma certification enhances career prospects and process efficiency.
✅ Certification levels range from White Belt (beginner) to Master Black Belt (expert).
✅ The DMAIC framework is the backbone of Lean Six Sigma methodology.
✅ Certification provides benefits like cost reduction, quality enhancement, and data-driven decision-making.
✅ Getting certified involves training, exams, and real-world project application.








