Introduction: Why Reducing Process Variation Matters
Process variation is one of the biggest roadblocks to achieving consistency, quality, and efficiency in any industry. Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, or service processes, uncontrolled variation leads to defects, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction.
Example: In a manufacturing plant, variation in assembly line operations can result in defective products, increased waste, and costly rework.
Lean Six Sigma provides a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and reducing variation. In this guide, we’ll walk through:
✔ What process variation is and how it affects performance
✔ How to use DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to minimize variation
✔ Statistical tools for variation analysis
✔ A hypothetical case study with data-driven insights
Understanding Process Variation
Process variation refers to fluctuations in process outputs due to different factors such as machine settings, raw material quality, environmental conditions, or human error.
There are two types of variation:
1. Common Cause Variation: Inherent to the process (e.g., slight differences in machine output)
2. Special Cause Variation: Unexpected deviations due to external factors (e.g., power failure, incorrect material used)
Step-by-Step Guide: Using DMAIC to Reduce Process Variation
🔹 Step 1: Define – Identify the Problem
Key Question: What process is experiencing high variation?
Example Case Study: A car manufacturing company observes inconsistent welding strength in their production line. Weak welds lead to increased defects, costly rework, and customer complaints.
🔹 Step 2: Measure – Collect Data
Key Question: How much variation exists in the process?
Example Action Plan:
• Measure weld strength in kilonewtons (kN) from 100 sample welds
• Use Control Charts to track variation
• Calculate Process Capability (Cp & Cpk) to check if the process meets specifications
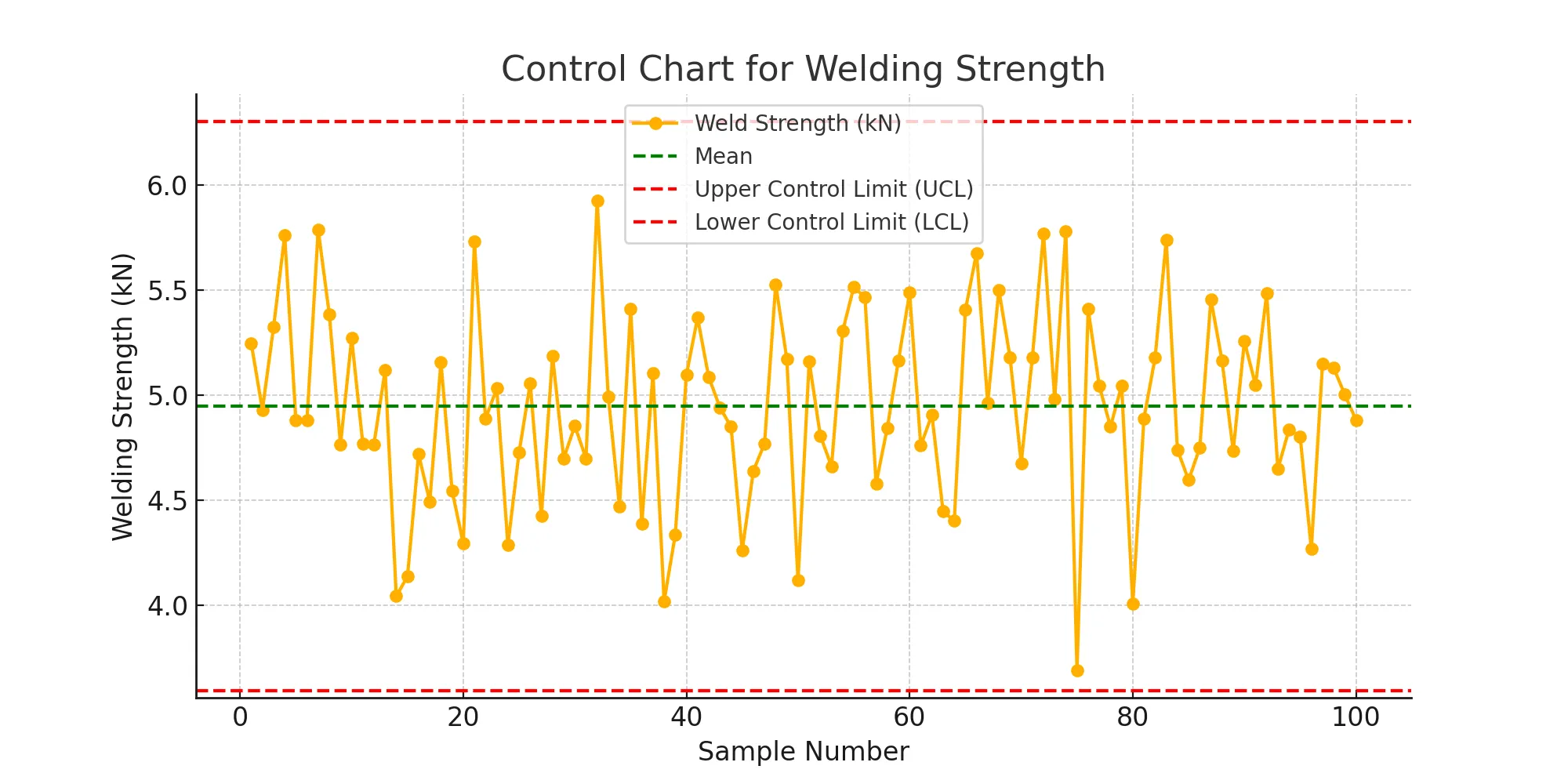
Control Chart
The chart shows that some weld strengths are approaching control limits, indicating process instability.
🔹 Step 3: Analyze – Identify Root Causes of Variation
Key Question: Why is the variation happening?
Example Action Plan:
• Conduct a Pareto Analysis to find the most common defects.
• Use a Fishbone (Ishikawa) Diagram to identify potential causes.
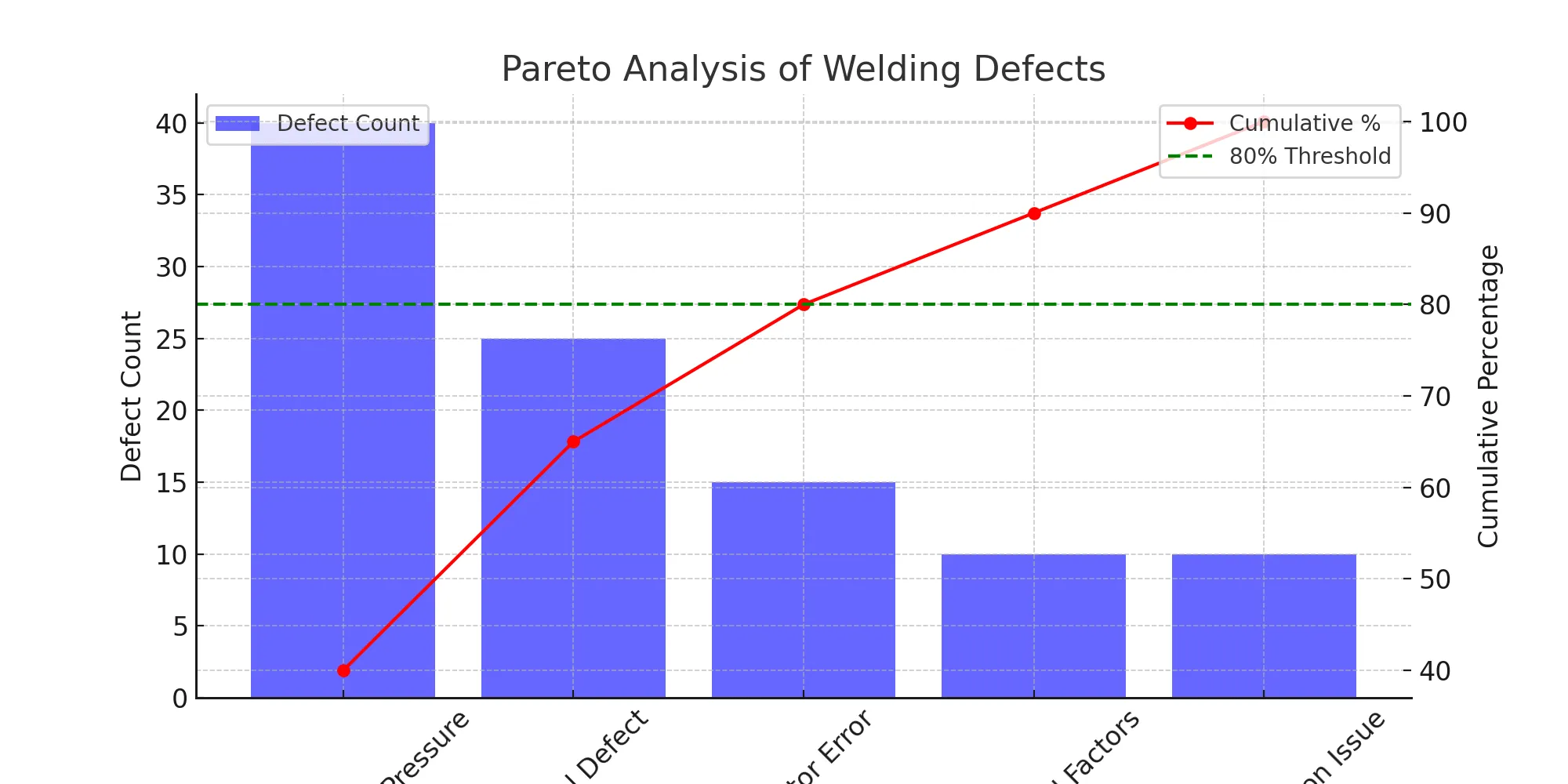
📊 Pareto Chart
This chart shows that ‘Incorrect Welding Pressure’ and ‘Material Defect’ account for 65% of defects, making them the primary focus for improvement.
🔹 Step 4: Improve – Implement Solutions
Key Question: How can we reduce variation?
Example Action Plan:
✅ Standardize Welding Pressure: Implement automatic pressure control to remove operator dependency.
✅ Supplier Quality Check: Tighten raw material inspection criteria to avoid defects.
✅ Training Program: Train operators on best practices to ensure consistency.
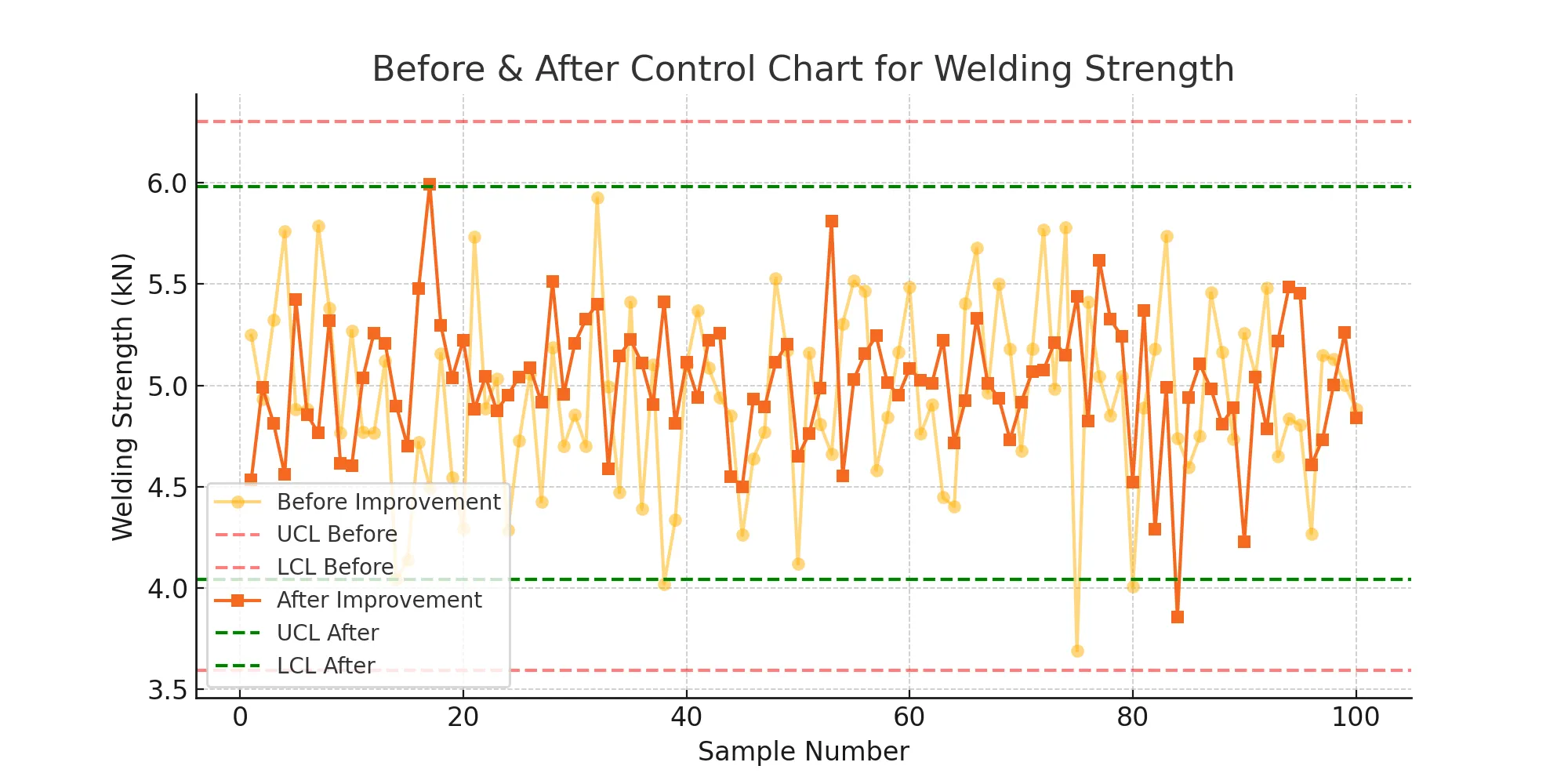
📊 Before & After Control Chart
Before improvement: High variation, with some points near control limits.
After improvement: Lower variation, with a more stable process.
🔹 Step 5: Control – Sustain the Improvements
Key Question: How do we maintain the reduced variation?
💡 Sustaining Actions:
✅ Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Document the improved process.
✅ Ongoing Monitoring: Use Control Charts to ensure process stability.
✅ Continuous Training: Keep operators trained on best practices.
✅ Supplier Audits: Regular quality checks on raw materials.
📌 Conclusion: The Power of Lean Six Sigma in Variation Reduction
Reducing process variation is critical for improving quality, reducing defects, and enhancing efficiency. Using the DMAIC approach, businesses can:
✔ Identify and measure variation
✔ Analyze root causes
✔ Implement targeted improvements
✔ Sustain gains through control mechanisms








